Meth Labs
October 2019
The asylum seekers interviewed at the bridge, requested anonymity, but otherwise spoke freely about current conditions in their home town. A small group from Ciudad Hidalgo, Michoacan explained that meth labs have popped up back home, drug abuse has skyrocketed and gangsters extort residents for payments of up to $2,000. Residents are fearful their children will be forced into the ranks of the drug gangs.
Meth Labs On The Increase Again
Instances of meth labs and methamphetamine trafficking and abuse in the United States are on the increase and it appears that opioid deaths are the trigger. As a result, this drug is having a devastating impact again on communities across the nation.
Clandestine production, Meth Labs, accounts for nearly all of the methamphetamine trafficked and abused in the United States. Domestic methamphetamine production, trafficking, and abuse are concentrated in the western, southwestern, and Midwestern United States. Methamphetamine is also increasingly available in portions of the South and the eastern United States, especially Georgia and Florida. Clandestine laboratories in California and Mexico are the primary sources of supply for methamphetamine available in the United States.
Meth Lab Injuries
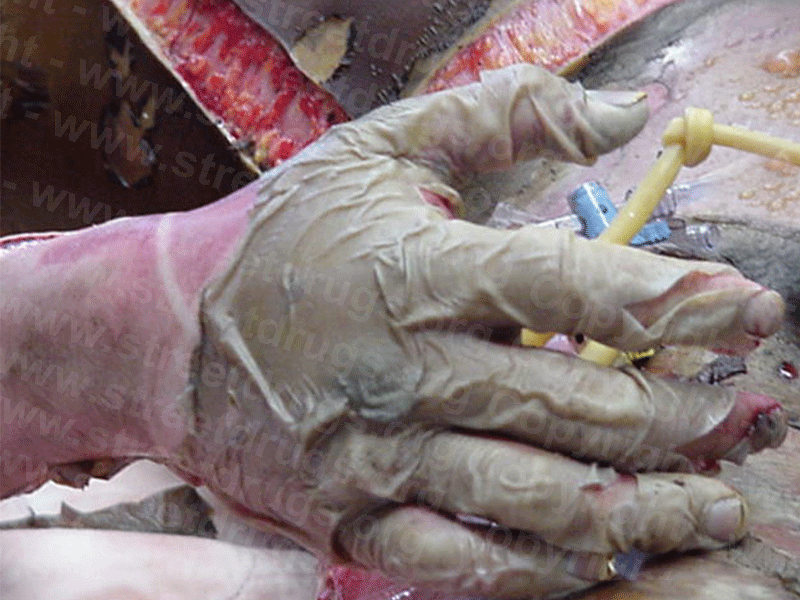
Injuries and deaths due to accidents or explosions in illegal methamphetamine labs are on the rise in the United States, a new study shows. Many of the injured were law enforcement and other First Responders, as well as children who lived in the home.
Meth labs are being discovered in remote areas of some of our national forests. These labs are an environmental hazard, the byproducts of meth labs contaminate the ground, lakes, and streams with harmful and highly explosive chemical compounds. Abandoned meth labs are basically time bombs, waiting for the single spark that can ignite the contents of the lab or a tourist visiting the park.
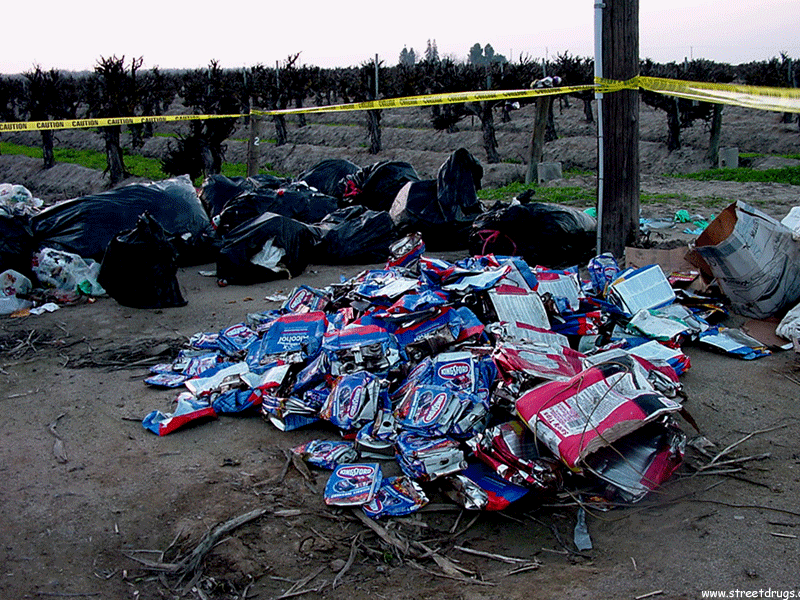
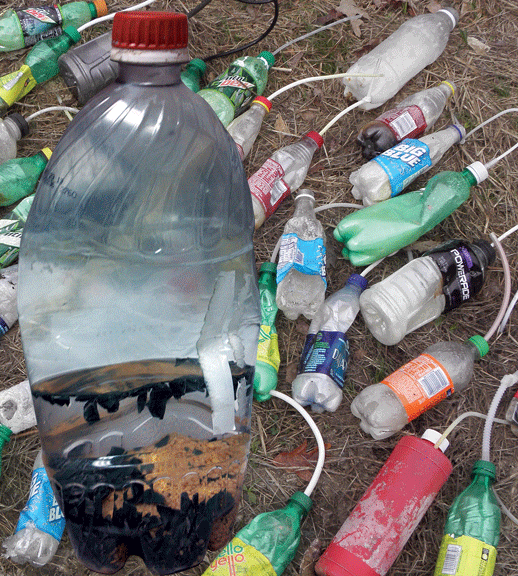
One-Pot Meth Labs
Meth labs of the past (referred to as garage labs) required hundreds or thousands of cold tablets, a large quantity of fuel, other household chemicals, glassware and other products and a room large enough to set up the lab. Making meth using the “one pot” method, is accomplished by pouring all the ingredients into a plastic soda bottle, or other container. The ingredients are then mixed by shaking (shake and bake) the container and regulating the pressure created by the chemical reaction of the cold tablets and household chemicals. The quantity of meth is small, usually enough for one or two doses, with quality varying.
Mexican Meth Labs
Mexican drug trafficking organizations have become the primary manufacturers and distributors of methamphetamine to cities throughout the United States, including in Hawaii. Domestic clandestine laboratory operators also produce and distribute meth but usually on a smaller scale. The methods used depend on the availability of precursor chemicals.
Currently, this domestic clandestinely produced meth is mainly made with diverted products that contain pseudoephedrine. Mexican methamphetamine is made with different precursor chemicals.
Source: DEA
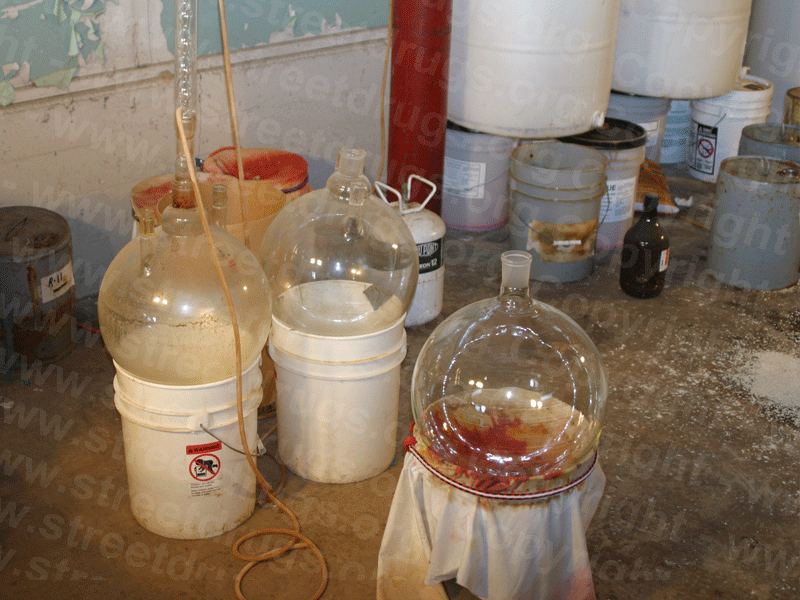
Methamphetamine is clandestinely manufactured in Meth Labs using the ephedrine or pseudoephedrine reduction method. In this process, over-the-counter cold and allergy tablets containing ephedrine or pseudoephedrine are placed in a solution of water, alcohol, or another solvent for several hours until the ephedrine or pseudoephedrine separates from the tablet. Then, using common household products and equipment listed on the following page and a recipe learned from friends or taken off the Internet, the ephedrine or pseudoephedrine is converted into high-quality Methamphetamine in makeshift, illegal labs by untrained individuals.
The state of Oregon requires a prescription to purchase certain over-the-counter medications that can be used to make methamphetamine. Other states are considering similar laws.
Household products contain most of the necessary chemicals to complete the manufacturing process. Certain brands of drain cleaner, for instance, have a high concentration of sulfuric acid. When mixed with table or rock salt, hydrogen chloride gas is produced for use in the final stage of methamphetamine production.
The hydrogen chloride gas procedure as well as other procedures are extremely dangerous and can cause death or serious injury not only to the individuals making the methamphetamine but to others who may be living in an adjoining house or apartment.
The chemicals used to make meth are toxic, and the lab operators routinely dump waste into streams, rivers, fields, and sewage systems. The chemical vapors produced during cooking permeate the walls and carpets of houses and buildings, making them uninhabitable. Cleaning up these sites requires specialized training and costs an average of $2,000-$4,000 per site in funds that come out of the already-strained budgets of state and local police.
Common Chemicals Used to Make Methamphetamine:
Alcohol (Isopropyl or rubbing alcohol)
Toluene (brake cleaner)
Ether (engine starter)
Sulfuric Acid (drain cleaner)
Red Phosphorus (matches/road flares)
Salt (table/rock)
Iodine (teat dip or flakes/crystal)
Lithium (batteries)
Trichloroethane (gun scrubber)
MSM (cutting agent)
Sodium Metal
Methanol/Alcohol (gasoline additives)
Muriatic Acid
Anhydrous Ammonia (farm fertilizer)
Sodium Hydroxide (lye)
Pseudoephedrine (cold tablets)
Ephedrine (cold tablets)
Acetone, Cat Litter
Typical Equipment Used to Make Methamphetamine:
Pyrex or Corning dishes (glass)
Jugs/bottles
Paper towels
Coffee filters
Thermometer
Cheesecloth
Funnels
Blenders
Rubber tubing/gloves
Pails/buckets
Gas Cans
Tape/clamps
Internet documents/notes
“How to Make Methamphetamine” books
Aluminum foil
Propane cylinders (20-lb)
Hotplates
Plastic storage containers/ice chests
Measuring cups
Towels/bed sheets
Laboratory beakers/glassware