By Bob Hansen
•
January 29, 2022
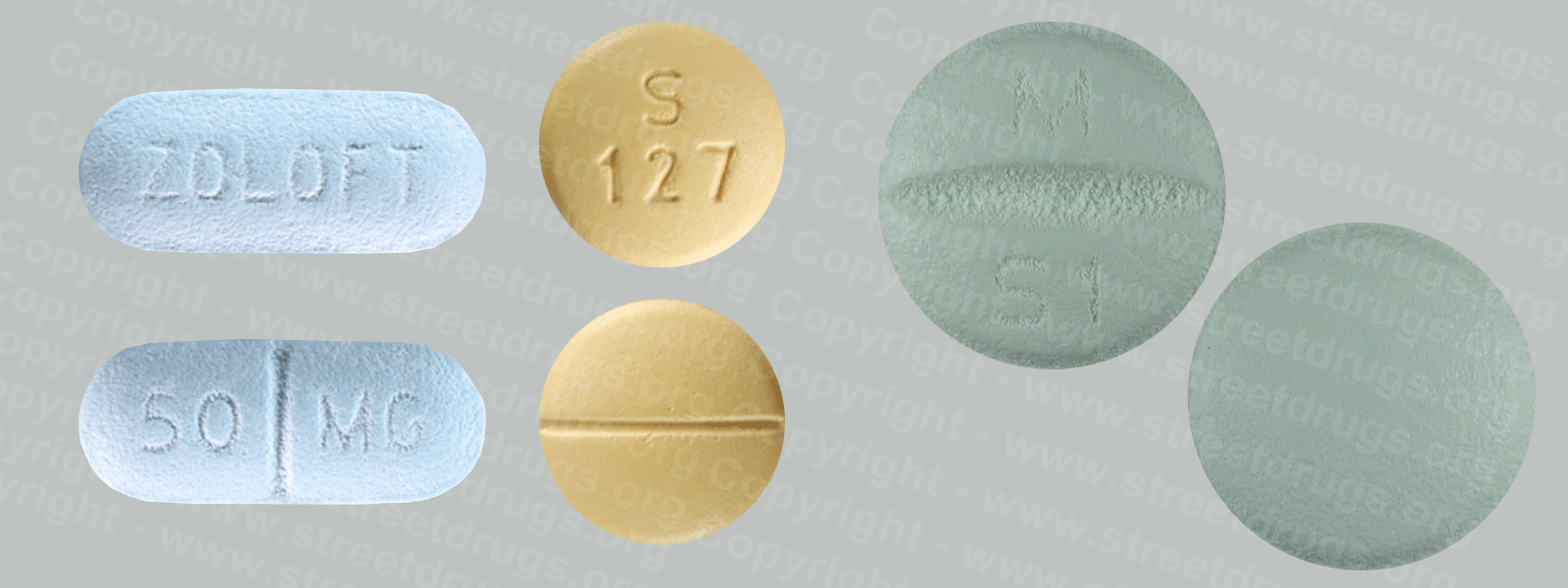
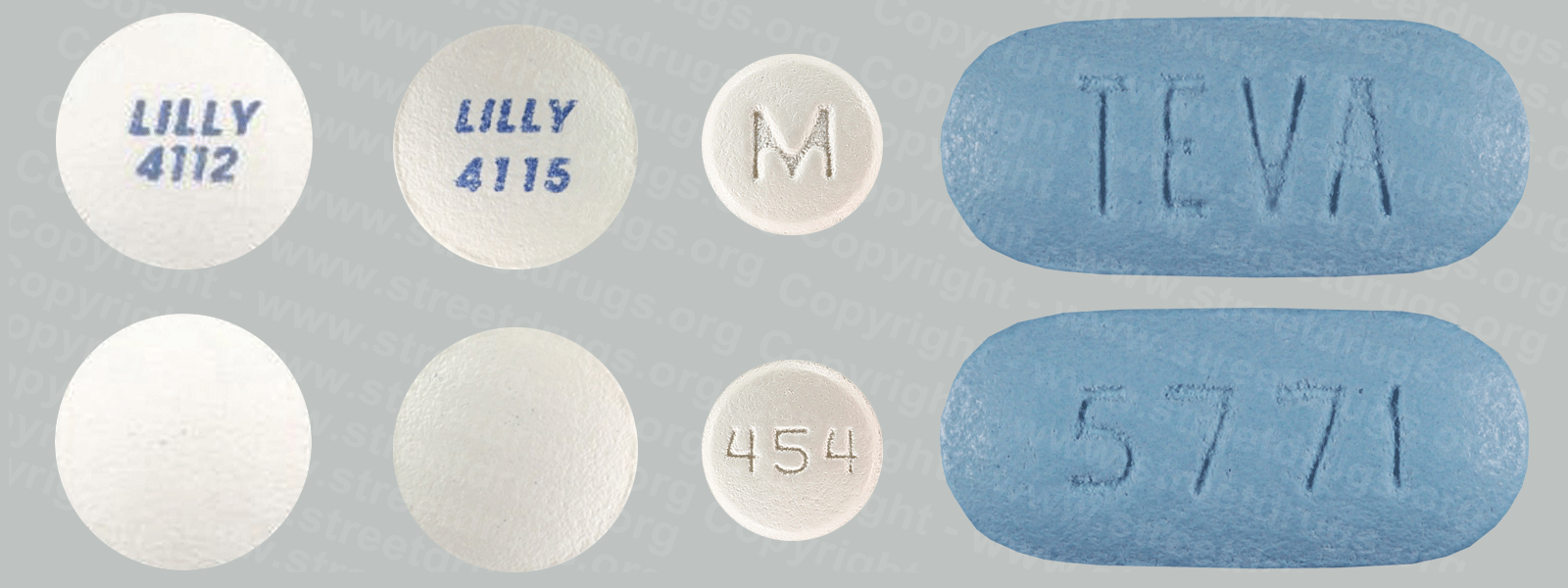
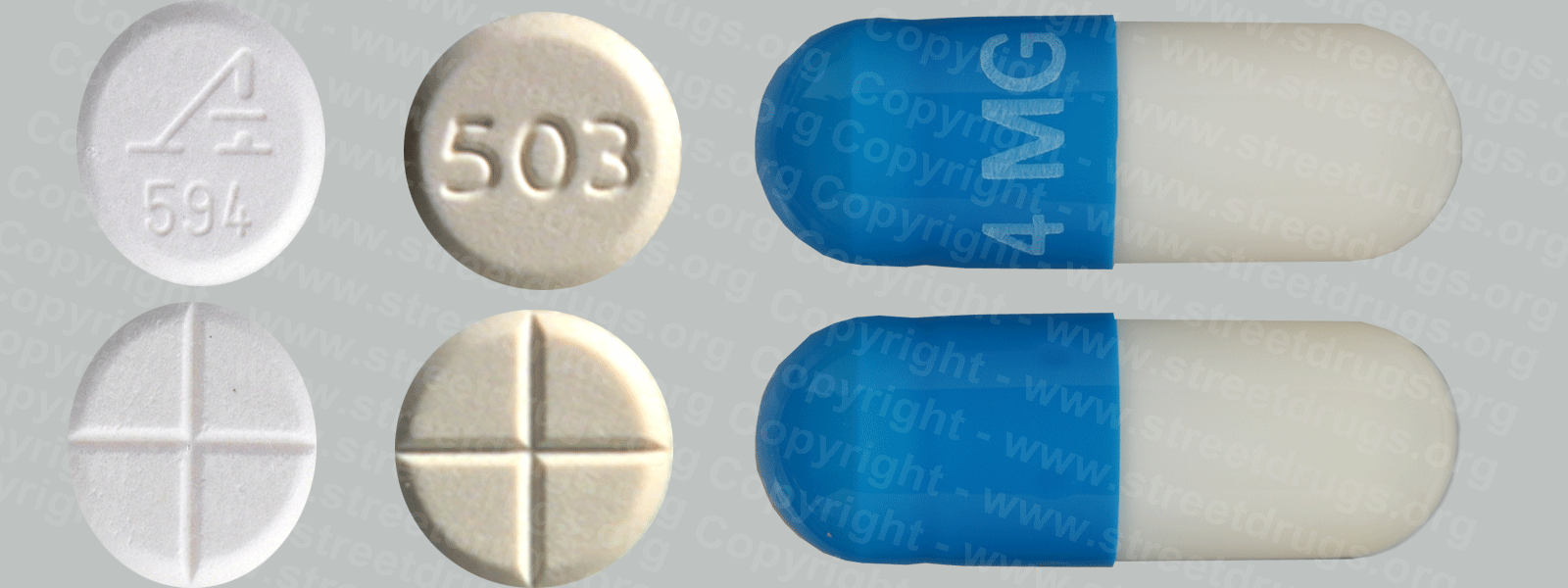
Zyprexa (Olanzapine) is used to treat the symptoms of psychotic conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. More information/images in the Prescription Drug Brochure. When you receive Zyprexa extended-release injection, the medication is usually released slowly into your blood over a period of time. However, when you receive olanzapine extended-release injection, there is a small chance that olanzapine may be released into your blood too quickly. If this happens, you may experience a serious problem called Post-injection Delirium Sedation Syndrome (PDSS). If you develop PDSS, you may experience dizziness, confusion, difficulty thinking clearly, anxiety, irritability, aggressive behavior, weakness, slurred speech, difficulty walking, muscle stiffness or shaking, seizures, drowsiness, and coma (loss of consciousness for a period of time). You are most likely to experience these symptoms during the first 3 hours after you receive the medication. You will receive Zyprexa extended-release injection in a hospital, clinic, or another medical facility where you can receive emergency medical treatment if it is needed. You will need to remain in the facility for at least 3 hours after you receive the medication. While you are in the clinic, the medical staff will watch you closely for signs of PDSS. When you are ready to leave the facility, you will need a responsible person to be with you, and you should not drive a car or operate machinery for the rest of the day. Get emergency medical help right away if you experience any symptoms of PDSS after you leave the facility. A program has been set up to help people receive Zyprexa extended-release injection safely. You will need to register and agree to the rules of this program before you receive olanzapine extended-release injection. Your doctor, the pharmacy that dispenses your medication, and the medical facility where you receive your medication will also need to register. Ask your doctor if you have any questions about this program. For people being treated with olanzapine extended-release injection or Zyprexa injection: Studies have shown that older adults with dementia (a brain disorder that affects the ability to remember, think clearly, communicate, and perform daily activities and that may cause changes in mood and personality) who take antipsychotics (medications for mental illness) such as olanzapine have an increased chance of death during treatment. Older adults with dementia may also have a greater chance of having a stroke or mini-stroke during treatment. Olanzapine injection and olanzapine extended-release injection are not approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of behavior disorders in older adults with dementia. Talk to the doctor who prescribed this medication if you, a family member, or someone you care for has dementia and is being treated with olanzapine injection or olanzapine extended-release injection. For more information visit the FDA website: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs Your doctor or pharmacist will give you the manufacturer’s patient information sheet (Medication Guide) when you begin treatment with olanzapine extended-release injection and each time you receive an injection. Read the information carefully and ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions. You can also visit the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) website (http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm085729.htm) or the manufacturer’s website to obtain the Medication Guide. extended-release injection, the medication is usually released slowly into your blood over a period of time. However, when you receive olanzapine extended-release injection, there is a small chance that olanzapine may be released into your blood too quickly. If this happens, you may experience a serious problem called Post-injection Delirium Sedation Syndrome (PDSS). If you develop PDSS, you may experience dizziness, confusion, difficulty thinking clearly, anxiety, irritability, aggressive behavior, weakness, slurred speech, difficulty walking, muscle stiffness or shaking, seizures, drowsiness, and coma (loss of consciousness for a period of time). You are most likely to experience these symptoms during the first 3 hours after you receive the medication. You will receive olanzapine extended-release injection in a hospital, clinic, or another medical facility where you can receive emergency medical treatment if it is needed. You will need to remain in the facility for at least 3 hours after you receive the medication. While you are in the clinic, the medical staff will watch you closely for signs of PDSS. When you are ready to leave the facility, you will need a responsible person to be with you, and you should not drive a car or operate machinery for the rest of the day. Get emergency medical help right away if you experience any symptoms of PDSS after you leave the facility. A program has been set up to help people receive olanzapine extended-release injection safely. You will need to register and agree to the rules of this program before you receive olanzapine extended-release injection. Your doctor, the pharmacy that dispenses your medication, and the medical facility where you receive your medication will also need to register. Ask your doctor if you have any questions about this program. For people being treated with olanzapine extended-release injection or olanzapine injection: Studies have shown that older adults with dementia (a brain disorder that affects the ability to remember, think clearly, communicate, and perform daily activities and that may cause changes in mood and personality) who take antipsychotics (medications for mental illness) such as olanzapine have an increased chance of death during treatment. Older adults with dementia may also have a greater chance of having a stroke or mini-stroke during treatment. Olanzapine injection and olanzapine extended-release injection are not approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of behavior disorders in older adults with dementia. Talk to the doctor who prescribed this medication if you, a family member, or someone you care for has dementia and is being treated with olanzapine injection or olanzapine extended-release injection. For more information visit the FDA website: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs Your doctor or pharmacist will give you the manufacturer’s patient information sheet (Medication Guide) when you begin treatment with olanzapine extended-release injection and each time you receive an injection. Read the information carefully and ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions. You can also visit the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) website (http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm085729.htm) or the manufacturer’s website to obtain the Medication Guide.